What’s Resistance Training? It’s more than just pumping iron; it’s a cornerstone of fitness, encompassing a range of techniques designed to build strength, endurance, and muscle mass. From lifting free weights to using resistance bands, the methods are diverse, each offering unique benefits and challenges. This exploration delves into the science, the practice, and the transformative power of resistance training, helping you understand how to incorporate it effectively into your life.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of resistance training, covering everything from fundamental principles and various methods to creating personalized workout plans and addressing common safety concerns. We’ll examine the numerous physical and mental health benefits, explore different equipment options, and offer practical advice on integrating resistance training into your daily routine regardless of your fitness level or experience.
Defining Resistance Training
Resistance training, also known as strength training or weight training, is a crucial component of a comprehensive fitness regimen. It involves performing exercises that require your muscles to work against a force, leading to increased strength, muscle mass, and overall physical fitness. Understanding its fundamental principles is key to maximizing its benefits and avoiding injury.Resistance training fundamentally works by placing controlled stress on the musculoskeletal system.
This stress, when appropriately managed, stimulates muscle growth (hypertrophy) and strengthens connective tissues like tendons and ligaments. The body adapts to this stress by building more muscle fibers and increasing the efficiency of neuromuscular communication – the connection between your nerves and muscles. This process is governed by the principles of progressive overload, specificity, and recovery. Progressive overload dictates gradually increasing the resistance or intensity of your workouts over time to continue challenging your muscles.
Specificity emphasizes that the type of training you perform directly influences the adaptations your body makes. Finally, adequate rest and recovery are crucial for muscle growth and repair.
Resistance Training Defined
Resistance training is any exercise that uses resistance to work your muscles. This resistance can come from weights, resistance bands, bodyweight, or even water. It’s a safe and effective way to improve your strength, build muscle, and enhance overall fitness, regardless of age or fitness level.
Types of Resistance Training Methods
Several methods exist for incorporating resistance training into a fitness plan, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right method depends on individual goals, experience level, and access to equipment.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free Weights (e.g., dumbbells, barbells) | Develops functional strength, improves balance and coordination, allows for a wide range of exercises. | Requires proper technique to avoid injury, can be more challenging for beginners. | Individuals with experience and proper guidance; those seeking functional strength. |
| Weight Machines | Easy to learn and use, isolates specific muscle groups, reduces risk of injury with proper form. | Limited range of motion compared to free weights, may not translate to real-world movements as effectively. | Beginners, individuals rehabilitating from injury, those targeting specific muscle groups. |
| Bodyweight Training (e.g., push-ups, squats, pull-ups) | Convenient, requires no equipment, improves body awareness and control. | Difficult to progressively overload, may not be suitable for all fitness levels or goals. | Beginners, individuals with limited access to equipment, those focusing on functional fitness. |
| Resistance Bands | Portable, affordable, provides variable resistance, suitable for various exercises. | Resistance can be less predictable than weights, may not be suitable for very heavy lifting. | Beginners, individuals with limited space or access to equipment, those seeking rehabilitation or supplemental training. |
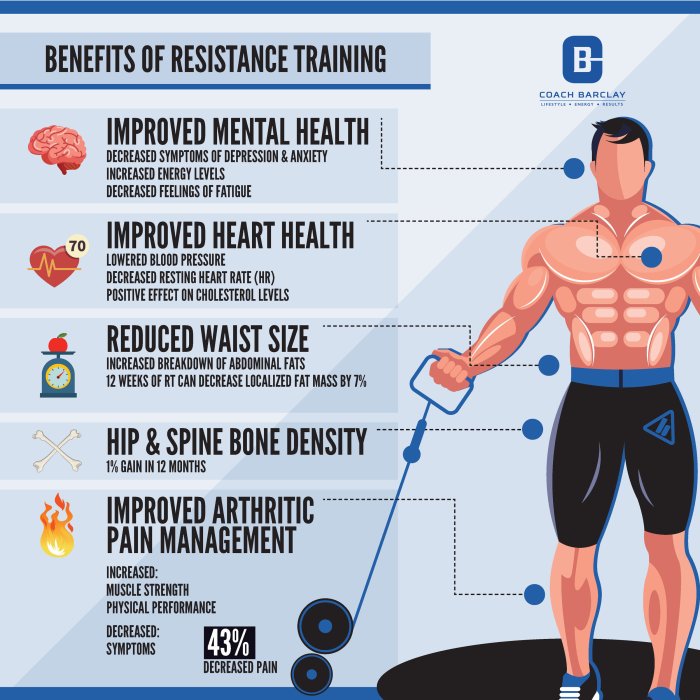
Benefits of Resistance Training

Resistance training, encompassing exercises that work against a force, offers a wide array of benefits extending far beyond enhanced physical capabilities. It profoundly impacts both physical and mental well-being, contributing to a healthier and more fulfilling life. The positive effects are well-documented across numerous studies, solidifying its place as a cornerstone of holistic health strategies.Resistance training triggers a cascade of physiological changes that translate into significant improvements in various aspects of physical health.
These benefits are not limited to athletes; individuals of all ages and fitness levels can reap the rewards.
Physical Benefits of Resistance Training
The impact of resistance training on physical health is substantial and multifaceted. It leads to increased muscle mass, enhanced strength, and improved endurance, contributing to a higher quality of life and reduced risk of age-related decline.
- Increased Muscle Mass (Hypertrophy): Resistance training stimulates muscle protein synthesis, leading to an increase in muscle fiber size and overall muscle mass. This process is crucial for maintaining metabolic rate, bone density, and overall functional capacity. Studies consistently demonstrate a positive correlation between resistance training and muscle hypertrophy, with gains dependent on factors such as training intensity, volume, and individual response.
- Enhanced Strength: The primary benefit of resistance training is the increase in muscular strength. This is achieved through both neural adaptations (improved coordination and recruitment of motor units) and hypertrophy (increased muscle size). Strength gains improve daily activities, reducing the risk of injuries from falls or strains, and enhancing athletic performance.
- Improved Muscular Endurance: Resistance training improves the ability of muscles to perform repeated contractions over a prolonged period. This is particularly beneficial for activities requiring sustained effort, such as climbing stairs or carrying groceries. Endurance gains are often seen alongside increases in strength and muscle mass.
Mental Health Benefits of Resistance Training
Beyond its physical advantages, resistance training significantly impacts mental well-being. It serves as a powerful tool for stress reduction and mood elevation, contributing to a more positive and resilient mental state.
- Stress Reduction: Resistance training has been shown to reduce levels of cortisol, a hormone associated with stress. The physical exertion involved acts as a natural stress reliever, promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety. Studies have shown that regular resistance training can be as effective as other stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga.
- Improved Mood: Resistance training stimulates the release of endorphins, natural mood boosters that alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. The sense of accomplishment and improved self-esteem associated with achieving fitness goals further contributes to enhanced mood and overall psychological well-being. Research indicates a strong correlation between regular exercise and a reduction in symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Evidence-Based Research Supporting the Benefits
Numerous peer-reviewed studies support the positive effects of resistance training on both physical and mental health. For instance, a meta-analysis published in the
- Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise* demonstrated the effectiveness of resistance training in increasing muscle mass and strength across diverse populations. Furthermore, research published in the
- Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology* has shown the efficacy of resistance training in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. These findings consistently highlight the significant contribution of resistance training to overall health and well-being.
Resistance Training Programs: What’s Resistance Training
Designing and implementing a resistance training program requires careful consideration of individual fitness levels, goals, and available resources. Effective programs incorporate progressive overload, ensuring continuous challenge and adaptation. The following Artikels sample programs and considerations for various fitness objectives.
Beginner Resistance Training Program
This program is designed for individuals with little to no prior resistance training experience. Focus is on proper form and building a foundational strength base. Each exercise should be performed with controlled movements, avoiding momentum. Rest for 60-90 seconds between sets.
Frequency: 2-3 days per week, with at least one day of rest between sessions.
Sets/Reps: 2-3 sets of 8-12 repetitions for each exercise.
| Exercise | Muscle Group |
|---|---|
| Squats | Legs |
| Push-ups (on knees if needed) | Chest, Shoulders, Triceps |
| Rows (using resistance bands or dumbbells) | Back, Biceps |
| Overhead press (using resistance bands or dumbbells) | Shoulders |
| Bicep curls (using resistance bands or dumbbells) | Biceps |
| Triceps extensions (using resistance bands or dumbbells) | Triceps |
Intermediate Resistance Training Program
This program builds upon the beginner program, incorporating progressive overload – gradually increasing the weight, reps, or sets over time to continually challenge the muscles. Proper form remains paramount to prevent injury. Rest periods should be adjusted based on individual recovery needs, potentially shortened to 45-60 seconds between sets for more advanced lifters.
Frequency: 3-4 days per week, with at least one day of rest between sessions. Consider a split routine targeting different muscle groups on different days.
Sets/Reps: 3-4 sets of 6-12 repetitions for each exercise. Progressive overload can be achieved by increasing weight, reps, or sets each week or every other week.
| Day | Exercise | Muscle Group |
|---|---|---|
| Monday (Legs & Shoulders) | Barbell Squats, Leg Press, Overhead Press, Lateral Raises | Legs, Shoulders |
| Tuesday (Chest & Back) | Bench Press, Dumbbell Flyes, Pull-ups (or Lat Pulldowns), Bent-Over Rows | Chest, Back |
| Wednesday (Rest) | ||
| Thursday (Legs & Shoulders) | Romanian Deadlifts, Lunges, Arnold Press, Front Raises | Legs, Shoulders |
| Friday (Chest & Back) | Incline Dumbbell Press, Cable Flyes, Seated Cable Rows, Face Pulls | Chest, Back |
| Saturday & Sunday (Rest) |
Resistance Training Programs for Different Fitness Goals, What’s Resistance Training
Different training programs are needed to achieve various fitness goals. These programs vary primarily in the rep ranges, sets, rest periods, and exercise selection.
Strength Training Program
Strength training focuses on maximal force production.
Sets/Reps: 1-5 sets of 1-5 repetitions. Focus on using heavy weights that challenge your maximal strength.
Rest: 3-5 minutes rest between sets.
Example exercises: Deadlifts, Squats, Bench Press, Overhead Press.
Hypertrophy Training Program
Hypertrophy, or muscle growth, requires a different stimulus than strength training.
Sets/Reps: 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions. Moderate weight, allowing for controlled movements through the full range of motion.
Rest: 60-90 seconds rest between sets.
Example exercises: Barbell Curls, Dumbbell Bench Press, Lat Pulldowns, Leg Extensions.
Endurance Training Program
Muscle endurance training focuses on the ability of muscles to perform repeated contractions over an extended period.
Sets/Reps: 3 sets of 15-20 repetitions. Lighter weight, maintaining good form throughout the entire range of motion.
Rest: 30-60 seconds rest between sets.
Example exercises: Push-ups, Pull-ups, Squats, Lunges (bodyweight or light weights).
Exercises for Major Muscle Groups
Chest: Bench Press, Incline Dumbbell Press, Decline Dumbbell Press, Push-ups, Cable Flyes.
Back: Pull-ups, Lat Pulldowns, Bent-Over Rows, Seated Cable Rows, Face Pulls.
Legs: Squats, Deadlifts, Lunges, Leg Press, Leg Extensions, Hamstring Curls.
Shoulders: Overhead Press, Lateral Raises, Front Raises, Arnold Press.
Biceps: Bicep Curls (barbell, dumbbell, hammer), Concentration Curls.
Triceps: Triceps Extensions (overhead, skullcrushers), Close-Grip Bench Press, Dips.
Ultimately, resistance training is a versatile and highly effective tool for improving overall health and well-being. Whether your goal is to build muscle, increase strength, enhance endurance, or simply improve your mood, a well-structured resistance training program, tailored to your individual needs and capabilities, can yield significant and lasting results. Remember to prioritize proper form, listen to your body, and consult with healthcare professionals as needed to ensure a safe and effective journey towards a stronger, healthier you.

