Resistance weights, encompassing dumbbells, barbells, weight machines, and resistance bands, are cornerstones of effective strength training. This guide delves into the diverse types of resistance training tools, outlining their advantages, disadvantages, and optimal applications for various fitness goals. We’ll explore comprehensive training programs suitable for beginners to advanced lifters, emphasizing proper form, injury prevention, and maximizing results.
From building muscle mass and increasing strength to improving endurance and aiding in rehabilitation, resistance weight training offers a versatile approach to fitness. We will cover everything from crafting effective workout routines and understanding proper technique to addressing common mistakes and mitigating injury risks. This comprehensive resource equips you with the knowledge to safely and effectively integrate resistance training into your fitness journey.
Resistance Weight Training Programs
Resistance weight training offers a highly effective method for building strength, increasing muscle mass, and improving overall fitness. Properly structured programs are crucial for maximizing results and minimizing the risk of injury. This section details sample programs for various experience levels, emphasizing progressive overload and targeted muscle group development.
Beginner Full-Body Resistance Weight Training Program, Resistance Weights
This program is designed for individuals new to weight training. Focus is on proper form and building a foundational level of strength. Each exercise should be performed with controlled movements, avoiding momentum.
| Exercise | Sets | Reps | Rest (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squats | 3 | 10-12 | 60 |
| Push-ups (on knees if needed) | 3 | As many as possible (AMRAP) | 60 |
| Rows (using resistance bands or dumbbells) | 3 | 10-12 | 60 |
| Overhead Press (using dumbbells or resistance bands) | 3 | 10-12 | 60 |
| Plank | 3 | 30-60 seconds | 60 |
Intermediate Hypertrophy-Focused Resistance Weight Training Program (Upper/Lower Split)
This program emphasizes muscle growth through higher volume and strategic exercise selection. The upper/lower split allows for adequate recovery between workouts. Progressive overload is achieved by gradually increasing weight, reps, or sets over time.
Upper Body (Monday):
| Exercise | Sets | Reps | Rest (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bench Press | 4 | 8-12 | 90 |
| Overhead Press | 4 | 8-12 | 90 |
| Barbell Rows | 4 | 8-12 | 90 |
| Bicep Curls | 3 | 10-15 | 60 |
| Triceps Extensions | 3 | 10-15 | 60 |
Lower Body (Wednesday):
| Exercise | Sets | Reps | Rest (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squats | 4 | 8-12 | 90 |
| Romanian Deadlifts | 4 | 10-15 | 90 |
| Leg Press | 3 | 12-15 | 60 |
| Hamstring Curls | 3 | 12-15 | 60 |
| Calf Raises | 3 | 15-20 | 60 |
Advanced Resistance Weight Training Program with Progressive Overload
This program incorporates advanced techniques and variations to continually challenge the muscles and promote growth. Progressive overload is implemented through a variety of methods, including increasing weight, reps, sets, decreasing rest periods, and incorporating more challenging exercise variations. Proper form is paramount to prevent injury.
Example Week (focus on one muscle group per day):
- Monday (Chest): Incline Dumbbell Press (4×8-12), Decline Dumbbell Press (3×10-15), Cable Flyes (3×12-15), Push-ups (3xAMRAP)
- Tuesday (Back): Pull-ups (4xAMRAP), Barbell Rows (4×8-12), T-Bar Rows (3×10-15), Face Pulls (3×15-20)
- Wednesday (Legs): Squats (4×6-8), Deadlifts (1×5, 1×3, 1×1), Leg Press (3×12-15), Leg Extensions (3×15-20)
- Thursday (Shoulders): Overhead Press (4×8-12), Lateral Raises (3×12-15), Front Raises (3×12-15), Reverse Flyes (3×15-20)
- Friday (Arms): Barbell Curls (4×8-12), Hammer Curls (3×10-15), Triceps Pushdowns (3×12-15), Skullcrushers (3×10-15)
Resistance Weight Training Programs Targeting Specific Muscle Groups
Targeted programs allow for focused development of individual muscle groups. These examples demonstrate the principles of exercise selection and rep ranges for effective hypertrophy.
Chest:
- Bench Press variations (Incline, Decline, Flat)
- Dumbbell Flyes
- Cable Crossovers
- Push-ups (various hand placements)
Back:
- Pull-ups (various grips)
- Barbell Rows
- T-Bar Rows
- Lat Pulldowns
- Face Pulls
Legs:
- Squats (various stances)
- Deadlifts (conventional, sumo)
- Leg Press
- Leg Extensions
- Hamstring Curls
- Calf Raises
Resistance Weight Training and Different Fitness Goals: Resistance Weights

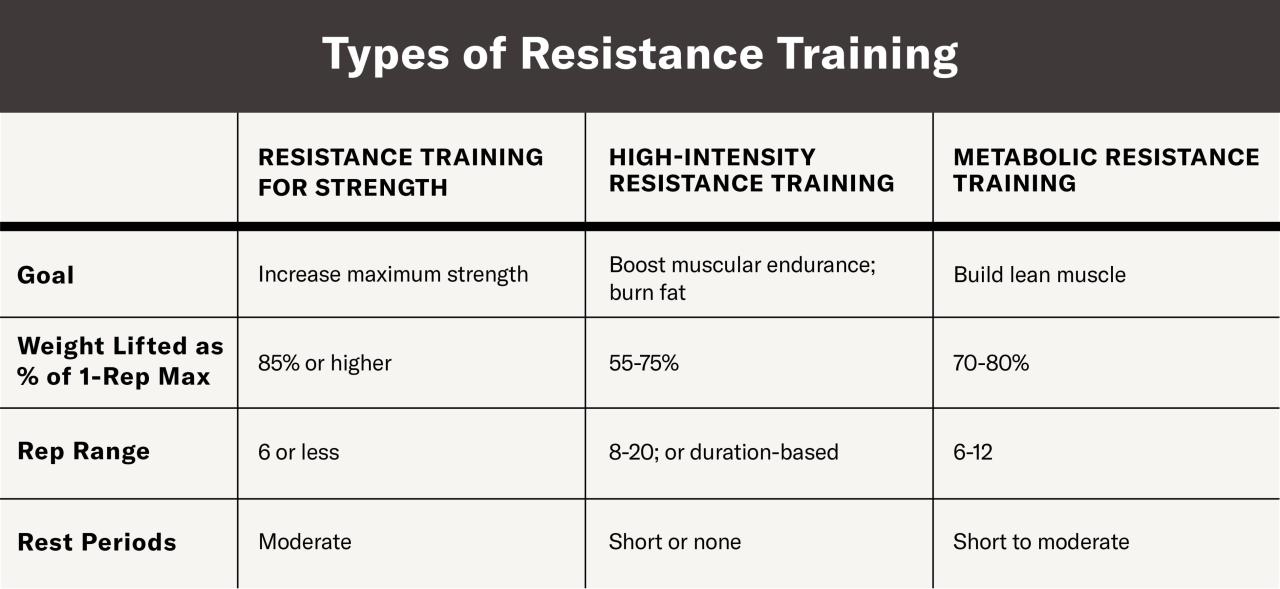
Resistance weight training, encompassing a broad spectrum of exercises utilizing weights or resistance bands, offers a versatile approach to achieving diverse fitness objectives. Its effectiveness stems from the principle of progressive overload, where muscles are systematically challenged to adapt and grow stronger. This adaptable nature makes it suitable for individuals ranging from elite athletes seeking peak performance to those recovering from injuries.Resistance weight training’s impact varies significantly depending on the specific program design.
Factors such as the intensity, volume, and type of exercises employed directly influence the outcome, shaping whether the primary benefit is increased muscle mass, enhanced strength, improved endurance, or a combination thereof.
Building Muscle Mass
Hypertrophy, or muscle growth, is achieved through high-volume training with moderate weight. This typically involves multiple sets (8-12) of repetitions (reps) performed to near-muscle failure. Exercises focusing on larger muscle groups, such as squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and overhead presses, are particularly effective for stimulating muscle protein synthesis and subsequent growth. Consistent adherence to a well-structured program, coupled with adequate protein intake, is crucial for maximizing muscle growth.
Improving Strength
Strength gains are primarily determined by the intensity of the training. Lower repetitions (1-5 reps) with heavier weights are more effective for enhancing neuromuscular efficiency and increasing maximal strength. Focus should be placed on compound exercises that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, optimizing the recruitment of motor units and improving overall strength capacity. Progressive overload, consistently increasing the weight or resistance over time, is vital for continuous strength development.
Enhancing Endurance
While traditionally associated with cardiovascular exercise, resistance training can significantly contribute to muscular endurance. Higher repetitions (15-20 reps) with lighter weights, performed in a circuit training fashion, effectively improve the capacity of muscles to sustain prolonged exertion. This type of training enhances the oxidative capacity of muscle fibers, improving their ability to utilize oxygen and delay fatigue. Functional exercises, mimicking real-life movements, can further enhance endurance relevant to daily activities.
Weight Loss and Overall Fitness
Resistance weight training plays a crucial role in weight management and overall fitness. It increases resting metabolic rate, meaning the body burns more calories even at rest. This is due to the increased muscle mass, which is metabolically more active than fat tissue. Furthermore, resistance training improves body composition by reducing body fat percentage and increasing lean muscle mass.
Combined with a balanced diet, it provides a holistic approach to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Rehabilitation and Injury Recovery
Resistance weight training is a cornerstone of many rehabilitation programs. It helps restore muscle strength, improve joint stability, and enhance functional mobility after injury or surgery. Therapists carefully design programs tailored to the specific needs of the patient, gradually increasing the intensity and complexity of exercises as the individual recovers. Proper form and progression are paramount to prevent re-injury and promote successful rehabilitation.
Resistance Weight Training Program Summary
| Fitness Goal | Exercise Examples | Sets/Reps | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Build Muscle Mass | Squats, Bench Press, Deadlifts, Bicep Curls, Triceps Extensions | 3-4 sets of 8-12 reps | Increased muscle size, improved strength, enhanced metabolism |
| Improve Strength | Squats, Deadlifts, Bench Press, Overhead Press, Power Cleans | 3-5 sets of 1-5 reps | Increased maximal strength, improved power output, enhanced neuromuscular efficiency |
| Enhance Endurance | Circuit training with bodyweight exercises or light weights (push-ups, lunges, rows, etc.) | 3-4 sets of 15-20 reps | Improved muscular endurance, increased cardiovascular fitness, reduced fatigue |
| Weight Loss & Overall Fitness | Combination of compound and isolation exercises, incorporating cardiovascular elements | Varied depending on specific program | Increased metabolism, improved body composition, enhanced overall fitness, improved bone density |
| Rehabilitation & Injury Recovery | Exercises tailored to specific injury, starting with low weight and gradually increasing | Varied depending on rehabilitation phase and injury | Improved muscle strength, enhanced joint stability, restored functional mobility |
Mastering resistance weight training involves understanding the nuances of different equipment, designing personalized programs, and prioritizing proper form. By combining knowledge of various training methods with a commitment to safety and progressive overload, individuals can unlock their full physical potential and achieve their fitness objectives. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new workout regimen.

