Resistance training helps unlock significant health benefits, extending far beyond enhanced muscle mass. It profoundly impacts bone density, cardiovascular health, and overall fitness. Unlike purely cardio-focused regimens, resistance training builds strength, improves metabolism, and fosters a body composition shift towards lean muscle. This comprehensive guide explores the various types of resistance training, suitable programs for diverse fitness goals, and crucial aspects of proper form and recovery to maximize results.
From designing personalized programs for weight loss or athletic enhancement to addressing the specific needs of seniors, we delve into the science behind muscle growth, the importance of nutrition, and strategies to overcome common barriers to consistent training. We also cover the practical aspects, including equipment usage, common mistakes to avoid, and the value of professional guidance.
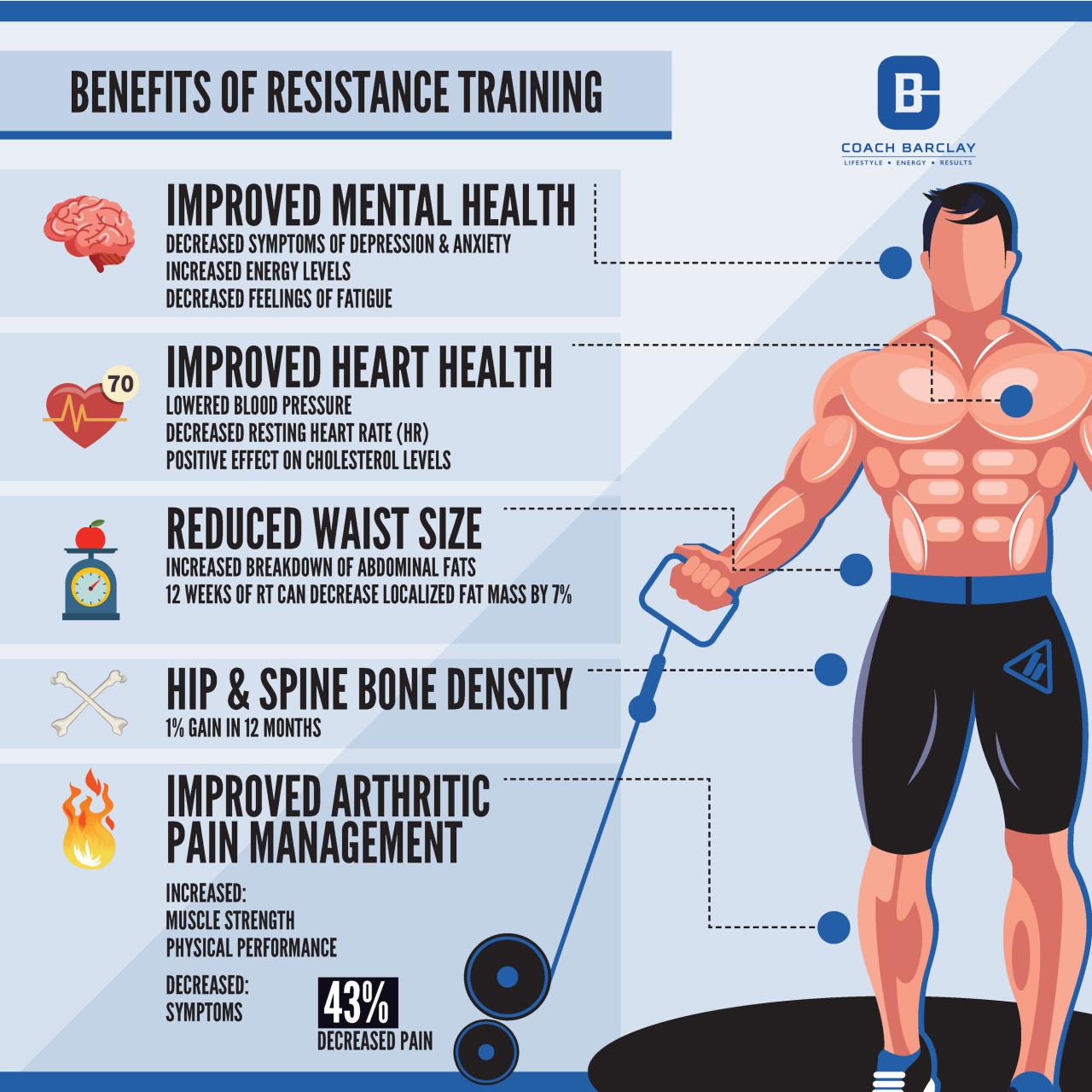
Benefits of Resistance Training
Resistance training, also known as strength training, offers a multitude of benefits extending far beyond increased muscle size and strength. It’s a cornerstone of a comprehensive fitness regimen, impacting physiological processes at a cellular level and contributing significantly to overall health and well-being. This exploration will delve into the mechanisms behind these benefits and compare resistance training’s impact to other forms of exercise.
Physiological Mechanisms of Muscle Growth and Strength
Resistance training stimulates muscle hypertrophy, the increase in muscle fiber size, and hyperplasia, a potential increase in the number of muscle fibers, though the latter’s extent in humans remains a subject of ongoing research. The process begins with muscle damage incurred during the training session. This damage triggers a series of cellular responses, including inflammation and the release of growth factors.
These factors, combined with the body’s natural repair mechanisms, lead to the synthesis of new muscle proteins, resulting in increased muscle size and strength. Crucially, the body adapts to the imposed stress, making muscles stronger and more resilient to future challenges. The magnitude of these adaptations depends on several factors, including training intensity, volume, and the individual’s genetic predisposition.
Effects on Bone Density and Cardiovascular Health
Resistance training plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, particularly important as we age. The stress placed on bones during weight-bearing exercises stimulates bone remodeling, leading to increased bone mineral density. Moreover, resistance training favorably impacts cardiovascular health. Studies demonstrate improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and insulin sensitivity, contributing to a reduced risk of heart disease.
This positive impact is linked to increased metabolic rate, improved blood vessel function, and enhanced insulin sensitivity, all contributing to a healthier cardiovascular system.
Comparison with Other Forms of Exercise
While cardiovascular exercise, such as running or swimming, is vital for improving cardiovascular health and endurance, resistance training offers unique benefits. Cardio primarily focuses on improving the efficiency of the cardiovascular system and increasing endurance, whereas resistance training directly builds muscle mass and strength. A balanced approach incorporating both cardio and resistance training is optimal for comprehensive fitness.
Cardiovascular exercise alone may not sufficiently address muscle loss associated with aging or inactivity, while resistance training alone might not sufficiently improve cardiovascular fitness. The synergistic effects of combining both types of exercise are widely recognized and recommended.
Examples of Resistance Training Exercises, Resistance Training Helps
A diverse range of exercises can be incorporated into a resistance training program, catering to various fitness levels and goals. The following table provides examples:
| Exercise Type | Muscles Worked | Equipment Needed | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squats | Quads, Glutes, Hamstrings | Bodyweight or Barbell | Beginner to Advanced |
| Push-ups | Chest, Triceps, Shoulders | Bodyweight | Beginner to Advanced (variations available) |
| Dumbbell Rows | Back, Biceps | Dumbbells | Beginner to Advanced |
| Overhead Press | Shoulders, Triceps | Dumbbells or Barbell | Beginner to Advanced |
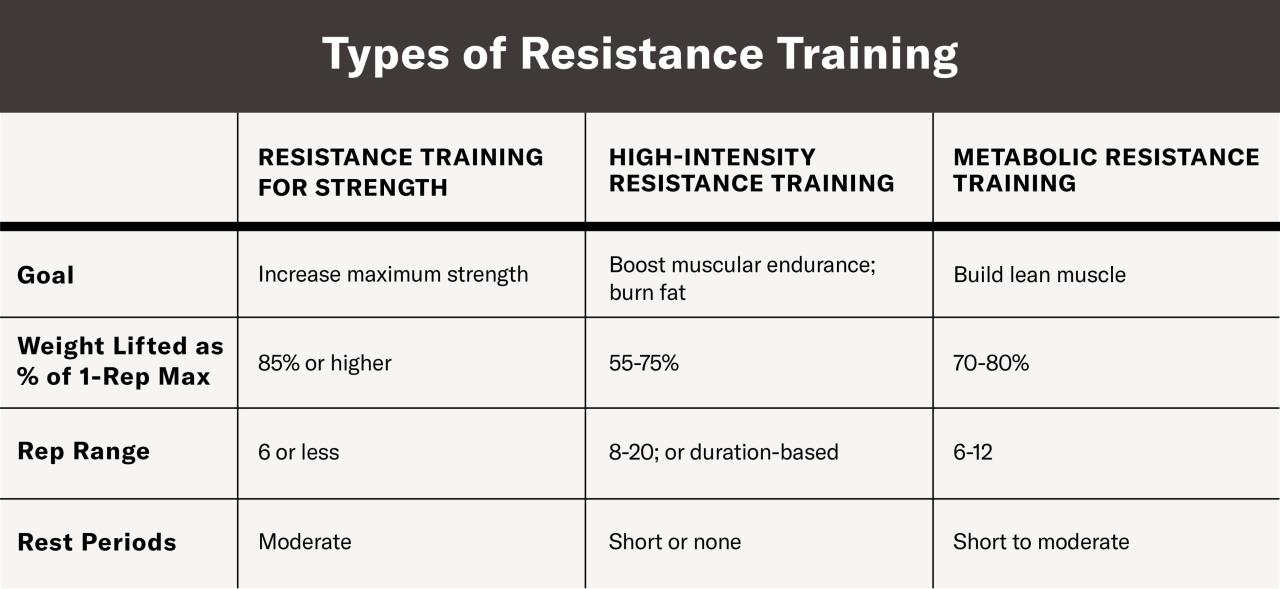
Resistance Training Programs for Different Goals
Resistance training, encompassing exercises using weights or resistance bands, offers diverse benefits depending on program design. Tailoring programs to specific objectives maximizes results, whether the goal is weight loss, enhanced athletic performance, or improved functional strength in older adults. The following Artikels sample programs, highlighting key considerations for each target population.
Weight Loss Resistance Training Program
This program focuses on maximizing calorie expenditure through compound movements while incorporating muscle building to boost metabolism. A higher rep range with shorter rest periods promotes both fat burning and muscle hypertrophy.
Day 1: Upper Body
- Bench Press: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Overhead Press: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Bent-Over Rows: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Bicep Curls: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Triceps Extensions: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
Day 2: Lower Body
- Squats: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Deadlifts: 1 set of 5 reps, 1 set of 3 reps, 1 set of 1 rep (increase weight each set)
- Lunges: 3 sets of 10-12 reps per leg
- Calf Raises: 3 sets of 15-20 reps
Day 3: Rest or Active Recovery (light cardio)
Repeat this cycle throughout the week, ensuring adequate rest between workouts. This program should be combined with a calorie-controlled diet for optimal weight loss.
Athletic Performance Enhancement Resistance Training Program
This program prioritizes power and speed development, crucial for many athletic endeavors. It incorporates plyometrics and Olympic lifts, emphasizing explosive movements and shorter rest periods to improve power output.
Day 1: Power Focus
- Power Cleans: 3 sets of 3 reps
- Hang Cleans: 3 sets of 3 reps
- Box Jumps: 3 sets of 5 reps
- Medicine Ball Throws: 3 sets of 5 reps
Day 2: Strength and Speed Focus
- Squats: 3 sets of 5 reps (heavy weight)
- Bench Press: 3 sets of 5 reps (heavy weight)
- Deadlifts: 1 set of 5 reps, 1 set of 3 reps, 1 set of 1 rep (increasing weight)
- Sprint Intervals: 6-8 repetitions of 40-yard sprints with adequate rest.
Day 3: Rest or Active Recovery (light cardio and mobility work)
This program requires proper technique and should be supervised by a qualified coach, especially for Olympic lifts. Adequate rest is crucial for recovery and preventing injury.
Senior-Focused Resistance Training Program
This program emphasizes safety and functional strength, crucial for maintaining independence and preventing falls in older adults. It focuses on compound movements with lighter weights and controlled movements to minimize injury risk.
Day 1: Upper Body
- Chair Dips: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Wall Push-Ups: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Bicep Curls (light weights): 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Overhead Press (light weights): 3 sets of 12-15 reps
Day 2: Lower Body
- Bodyweight Squats: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Standing Calf Raises: 3 sets of 15-20 reps
- Step-Ups: 3 sets of 10-12 reps per leg
Day 3: Rest or Active Recovery (gentle stretching and walking)
This program should be adjusted based on individual fitness levels and any pre-existing conditions. Consulting a physician or physical therapist before starting any new exercise program is recommended for seniors.
Elements of a Resistance Training Program
A well-structured resistance training program incorporates several key elements:
- Warm-up: 5-10 minutes of light cardio, such as jogging or jumping jacks, followed by dynamic stretching, such as arm circles and leg swings, to prepare the muscles for exercise.
- Workout Sets & Reps: The number of sets and repetitions depends on the training goal. Higher reps (12-15) are generally used for hypertrophy, while lower reps (1-5) are used for strength gains. The weight used should be challenging but allow for maintaining proper form.
- Cool-down: 5-10 minutes of static stretching, holding each stretch for 20-30 seconds, to improve flexibility and reduce muscle soreness.
- Rest periods: Rest periods between sets vary depending on the training goal. Shorter rest periods (30-60 seconds) are generally used for hypertrophy, while longer rest periods (2-3 minutes) are used for strength gains.
Nutrition and Recovery for Optimal Results: Resistance Training Helps
Resistance training, while effective in building muscle and strength, requires a strategic nutritional approach and sufficient recovery to maximize its benefits. Failing to adequately fuel your body and allow for proper rest will hinder progress and potentially lead to injury. This section Artikels the key dietary and lifestyle components crucial for optimal results from your resistance training program.
The Role of Protein in Muscle Growth and Recovery
Protein is the fundamental building block of muscle tissue. After a resistance training session, muscle fibers experience microscopic tears. Protein synthesis, the process of repairing and rebuilding these fibers, is crucial for muscle growth (hypertrophy) and recovery. Consuming sufficient protein provides the necessary amino acids to facilitate this process. A general recommendation is to consume 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily for individuals engaging in resistance training.
This intake should be distributed throughout the day, with some protein consumed both before and after workouts to optimize muscle protein synthesis. A deficiency in protein intake can significantly impair muscle recovery and limit gains in strength and size.
The Importance of Hydration and Sleep
Adequate hydration is essential for optimal muscle function and recovery. Water is involved in numerous metabolic processes, including nutrient transport and waste removal. Dehydration can lead to reduced performance, increased fatigue, and impaired muscle recovery. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially before, during, and after workouts.Sleep is equally critical. During sleep, the body repairs and rebuilds tissues, including muscles.
Growth hormone, a crucial hormone for muscle growth and recovery, is primarily released during sleep. Insufficient sleep can disrupt hormone balance, impair muscle protein synthesis, and increase the risk of injury. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Example of a Balanced Diet Plan
A balanced diet supporting resistance training goals should include a variety of nutrient-rich foods. This example focuses on a single day, which should be adapted to individual caloric needs and preferences:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries, nuts, and a scoop of whey protein powder.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, quinoa, and avocado.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted vegetables (broccoli, sweet potatoes) and brown rice.
- Snacks: Greek yogurt with fruit, a protein bar, or a handful of almonds.
This plan emphasizes lean protein sources, complex carbohydrates for sustained energy, and healthy fats for hormone production and overall health. The portion sizes should be adjusted based on individual caloric requirements, which can be determined through consultation with a registered dietitian or using online calculators.
Supplements for Muscle Recovery and Growth
While a balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients for muscle growth and recovery, some individuals may choose to supplement their intake. Whey protein is a popular choice due to its high protein content and rapid absorption rate. Creatine monohydrate is another commonly used supplement that can enhance strength and power output. However, it’s crucial to remember that supplements should not replace a healthy diet, and potential drawbacks, such as gastrointestinal distress or interactions with medications, should be considered.
Always consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting any new supplement regimen. Furthermore, the effectiveness of supplements can vary significantly between individuals. Results are not guaranteed, and reliance on supplements alone is insufficient for achieving optimal results.
Ultimately, incorporating resistance training into a holistic fitness plan offers a powerful pathway to improved health and well-being. By understanding the principles of proper form, nutrition, and recovery, individuals can harness the transformative power of resistance training to achieve their fitness goals, regardless of age or experience level. Remember, consistency and proper technique are key to reaping the numerous benefits this impactful form of exercise offers.

