Muscle Training Exercises represent a cornerstone of physical fitness, offering a pathway to enhanced strength, improved physique, and overall well-being. This guide delves into the diverse world of muscle training, exploring various exercise types, program design strategies, and crucial considerations for safety and optimal results. From understanding proper form to tailoring workouts for different fitness levels, we provide a comprehensive framework for achieving your fitness goals.
We’ll examine the nuances of different training methodologies, emphasizing the importance of progressive overload and recovery for sustained progress.
We’ll cover everything from foundational bodyweight exercises to advanced weight training techniques, providing actionable strategies and insights backed by evidence-based practices. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or a complete beginner, this guide offers a wealth of knowledge to help you build a safe and effective muscle training program that aligns with your individual needs and aspirations. The information presented here is intended to serve as a starting point; always consult with a healthcare professional before embarking on any new fitness regimen.
Types of Muscle Training Exercises

Muscle training, encompassing a range of exercises designed to build strength and increase muscle mass, offers significant health benefits. The choice of training method depends on individual goals, experience level, and access to equipment. This section categorizes various muscle training exercises and analyzes their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Categorization of Muscle Training Exercises
The following table categorizes common muscle training exercises based on equipment and difficulty. Note that perceived difficulty is subjective and depends on individual fitness levels.
| Exercise Name | Muscle Group Targeted | Equipment Needed | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Push-ups | Chest, Triceps, Shoulders | Bodyweight | Beginner – Intermediate |
| Squats | Quads, Glutes, Hamstrings | Bodyweight | Beginner – Advanced |
| Lunges | Quads, Glutes, Hamstrings | Bodyweight | Beginner – Intermediate |
| Plank | Core | Bodyweight | Beginner – Advanced |
| Bench Press | Chest, Triceps, Shoulders | Barbell, Dumbbells, Bench | Beginner – Advanced |
| Deadlift | Back, Glutes, Hamstrings | Barbell | Intermediate – Advanced |
| Overhead Press | Shoulders, Triceps | Barbell, Dumbbells | Beginner – Advanced |
| Bicep Curls | Biceps | Dumbbells, Barbell | Beginner – Intermediate |
| Resistance Band Rows | Back, Biceps | Resistance Band | Beginner – Intermediate |
| Resistance Band Chest Press | Chest, Triceps | Resistance Band | Beginner – Intermediate |
Benefits and Drawbacks of Different Training Categories
Bodyweight exercises offer accessibility and convenience, requiring minimal equipment. However, progression can be limited without increasing the difficulty of the exercise. Weight training, using free weights or machines, allows for more precise muscle targeting and progressive overload, leading to significant strength gains. However, it requires proper form and technique to avoid injury. Resistance band exercises provide a versatile and portable option, offering variable resistance and reduced impact on joints.
However, the resistance may not be as substantial as free weights, limiting maximum strength gains.
Comparison of Weight Training Methods: Free Weights vs. Machines, Muscle Training Exercises
Free weights, such as dumbbells and barbells, engage more stabilizer muscles, improving overall balance and coordination. They also offer a greater range of motion and allow for more natural movement patterns. Machines, on the other hand, provide more stability and guidance, making them suitable for beginners or individuals recovering from injury. They often isolate specific muscle groups more effectively, but can limit functional strength development compared to free weights.
For example, a barbell squat engages more muscles and requires greater balance than a leg press machine, although both target similar muscle groups. The choice between free weights and machines depends on individual goals and experience levels. A well-rounded program often incorporates both.
Muscle Training for Different Fitness Levels: Muscle Training Exercises
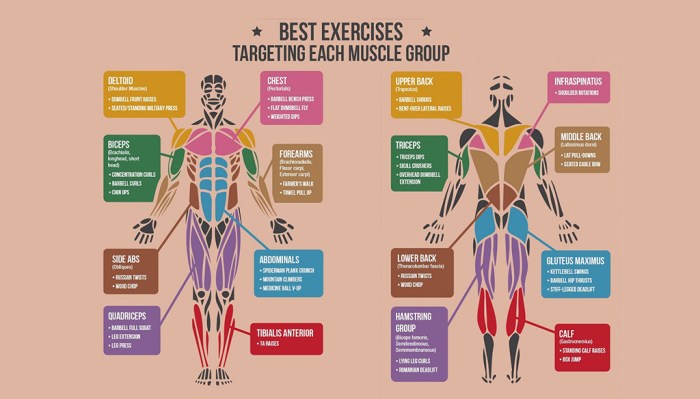
Tailoring muscle training programs to individual fitness levels is crucial for maximizing results and minimizing injury risk. A well-structured program considers the participant’s experience, physical capabilities, and overall fitness goals. Progression should be gradual, allowing the body to adapt and strengthen appropriately.
Exercise Selection Across Fitness Levels
The following table Artikels suitable exercises for beginners, intermediate, and advanced fitness levels, categorized by muscle group. Exercise modifications are key to ensuring safety and effectiveness at each stage.
| Muscle Group | Beginner | Intermediate | Advanced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legs | Bodyweight squats, wall sits, calf raises | Goblet squats, lunges, Romanian deadlifts (RDLs) with lighter weight | Barbell back squats, front squats, jump squats, Bulgarian split squats |
| Chest | Incline push-ups against a wall, push-ups on knees | Dumbbell bench press, incline dumbbell press | Barbell bench press, decline dumbbell press, dumbbell flyes |
| Back | Bent-over rows with resistance bands, supermans | Dumbbell rows, pull-ups (assisted if needed) | Barbell rows, pull-ups (weighted if possible), lat pulldowns |
| Shoulders | Overhead press with light dumbbells or resistance bands, lateral raises with light weights | Dumbbell shoulder press, lateral raises, front raises | Barbell overhead press, Arnold press, lateral raises with heavier weights |
| Arms (Biceps) | Bicep curls with resistance bands, hammer curls | Dumbbell bicep curls, concentration curls | Barbell bicep curls, incline dumbbell curls, hammer curls with heavier weight |
| Arms (Triceps) | Triceps dips on a chair, overhead triceps extensions with light dumbbells | Close-grip bench press, overhead dumbbell extensions, skullcrushers | Close-grip bench press with heavier weight, triceps pushdowns, overhead rope extensions |
Modifying Exercises for Different Fitness Levels and Limitations
Modifying exercises involves adjusting the intensity, range of motion, and support provided. Beginners may start with simpler variations, such as using resistance bands instead of free weights or performing exercises with assistance. Intermediate individuals can increase the weight or resistance, while advanced individuals can incorporate more challenging variations and advanced techniques. For example, a beginner might perform squats against a wall for support, while an advanced individual might incorporate plyometrics such as jump squats.
Individuals with limitations may need to adjust their range of motion or utilize adaptive equipment.
Adjusting Intensity and Volume
Intensity refers to the weight or resistance used, while volume refers to the total amount of work performed (sets x reps). Beginners should focus on mastering proper form with lower intensity and volume, gradually increasing both as they get stronger. Intermediate individuals can increase intensity and volume more aggressively. Advanced individuals may incorporate advanced training techniques such as drop sets, supersets, and rest-pause sets to further challenge their muscles.
For instance, a beginner might perform 2 sets of 10-12 repetitions of squats, while an advanced individual might perform 5 sets of 5-8 repetitions with heavier weight. Regular monitoring of progress and adjusting the program accordingly is essential for continued improvement. Consider incorporating periodization, cycling the intensity and volume over time to prevent plateaus and overtraining.
Mastering muscle training involves a multifaceted approach that integrates proper exercise form, strategic program design, and mindful attention to nutrition and recovery. By understanding the principles Artikeld in this guide, individuals can embark on a transformative journey towards enhanced physical capabilities and overall well-being. Remember, consistency and progressive overload are key to achieving lasting results. Prioritizing safety and listening to your body’s signals are paramount to preventing injury and ensuring long-term success in your fitness pursuits.
This guide serves as a foundational resource, encouraging you to explore further and tailor your approach to meet your unique fitness goals.

