Weight Training Benefits extend far beyond simply building muscle. This rigorous physical activity profoundly impacts both physical and mental health, offering a holistic approach to wellness rarely matched by other fitness regimens. From boosting bone density and mitigating the risk of osteoporosis to significantly improving cardiovascular health and cognitive function, weight training provides a comprehensive suite of advantages.
Understanding these benefits is crucial for anyone seeking to optimize their overall well-being.
This exploration delves into the multifaceted advantages of weight training, examining its impact on physical strength and endurance, mental acuity, and stress reduction. We’ll also cover program design, nutritional considerations, and safety protocols to ensure you can harness the power of weight training safely and effectively. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or a complete beginner, the information presented here will empower you to make informed decisions about integrating weight training into your lifestyle.
Safety and Considerations in Weight Training: Weight Training Benefits
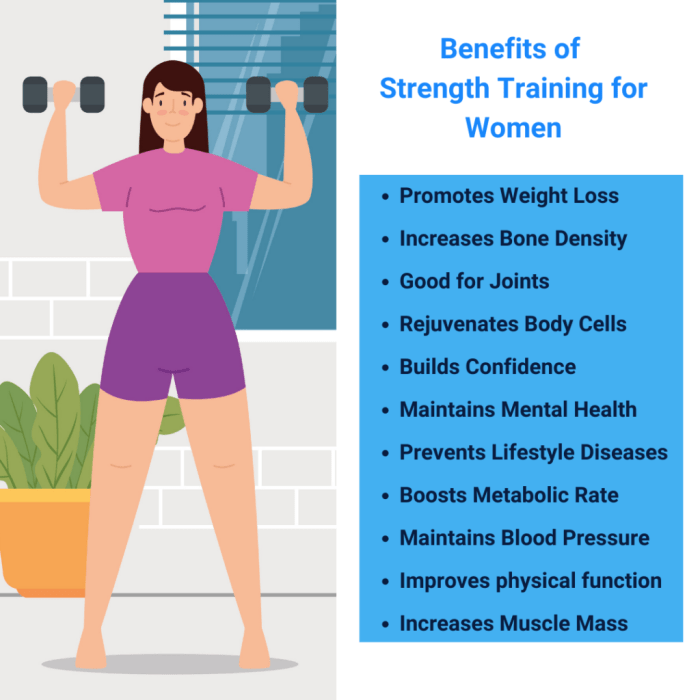
Weight training, while offering significant health benefits, carries inherent risks if not approached with caution and proper technique. Understanding and mitigating these risks is crucial for maximizing the benefits while minimizing the potential for injury. This section Artikels key safety considerations and preventative measures for a safe and effective weight training regimen.
Common Weight Training Injuries and Prevention
Muscle strains and sprains are prevalent injuries in weight training, often resulting from improper form, excessive weight, or insufficient warm-up. These injuries typically affect the lower back, hamstrings, shoulders, and knees. Prevention involves focusing on correct lifting techniques, gradually increasing weight loads, and prioritizing proper form over the amount of weight lifted. For example, performing squats with a rounded back significantly increases the risk of lower back injury, while maintaining a neutral spine minimizes this risk.
Similarly, using controlled movements and avoiding jerky motions helps prevent strains in the hamstrings and other muscle groups.
Warm-up and Cool-down Routines
A comprehensive warm-up is essential to prepare the body for the physical demands of weight training. This should include 5-10 minutes of light cardio, such as jogging or jumping jacks, followed by dynamic stretching, such as arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists. This increases blood flow to the muscles, improves flexibility, and reduces the risk of injury. A proper cool-down, consisting of 5-10 minutes of light cardio and static stretching, holding each stretch for 20-30 seconds, helps to reduce muscle soreness and promote recovery.
For instance, holding a hamstring stretch for 30 seconds after a leg workout helps to lengthen the muscles and improve flexibility.
Selecting Appropriate Weights and Adjusting Intensity
Choosing the right weight is paramount for safety and progress. Beginners should start with lighter weights, focusing on mastering proper form before gradually increasing the weight. A good rule of thumb is to select a weight that allows you to complete the prescribed number of repetitions with good form while feeling challenged. Progressive overload, gradually increasing the weight, repetitions, or sets over time, is key to building strength and muscle mass.
However, avoid increasing weight too rapidly, which can lead to injury. For example, if a lifter can comfortably perform 10 repetitions of a bench press with a particular weight, they might increase it slightly for the next workout, aiming for a challenging yet manageable weight.
Rest and Recovery to Prevent Overtraining, Weight Training Benefits
Adequate rest and recovery are critical for muscle growth and injury prevention. Overtraining, a condition characterized by persistent fatigue, decreased performance, and increased risk of injury, results from insufficient rest. Allowing muscles sufficient time to repair and rebuild is essential. This includes incorporating rest days into your training schedule and prioritizing sleep. The general recommendation is to allow at least one day of rest between weight training sessions for the same muscle groups.
For example, a weight training split focusing on different muscle groups each day allows for adequate recovery.
Proper Use of Safety Equipment
Weight belts can provide additional support for the lower back during heavy lifts, particularly compound exercises like squats and deadlifts. Spotters are crucial for exercises like bench presses and squats, ensuring a safe return to the starting position if the lifter fails to complete a repetition. Proper use of weight belts involves placing the belt snugly around the waist, ensuring it doesn’t restrict breathing.
Spotters should be positioned appropriately, ready to assist if necessary, avoiding unnecessary interference. Using collars on weight plates prevents them from sliding off the barbell, a crucial safety measure to avoid accidents. Finally, ensuring the weight training area is free of obstacles and distractions minimizes the risk of accidents.
Incorporating weight training into a well-rounded fitness plan offers a powerful pathway to improved physical and mental health. From strengthening bones and muscles to enhancing cognitive function and reducing stress, the benefits are undeniable. By understanding proper techniques, prioritizing nutrition, and adhering to safety guidelines, individuals can unlock the transformative potential of weight training, leading to a healthier, more resilient, and more fulfilling life.
The journey to a stronger, healthier you starts with a single lift.

