Weight Training Activities offer a powerful pathway to improved fitness, encompassing a diverse range of exercises targeting specific muscle groups. From building strength and muscle mass to enhancing fat loss and overall well-being, understanding the nuances of proper form, exercise selection, and program design is crucial. This guide delves into the intricacies of weight training, providing a structured approach for individuals of all fitness levels, addressing safety, nutrition, and modifications for specific populations.
We’ll explore various weight training activities, categorized by muscle group and difficulty, detailing their benefits and drawbacks. We’ll then craft sample programs tailored to distinct fitness goals—muscle building, strength gain, and fat loss—outlining exercises, sets, reps, and rest periods. Furthermore, we’ll cover proper form and technique for common exercises, highlighting common mistakes and their consequences. Crucially, we’ll emphasize safety precautions, injury prevention, and the importance of nutrition and recovery.
Finally, we’ll discuss weight training equipment, resources, and adaptations for specific populations, ensuring a holistic understanding of this transformative fitness modality.
Safety Precautions and Injury Prevention

Weight training, while offering significant health benefits, carries inherent risks of injury if proper precautions are not taken. Understanding common injuries and implementing preventative strategies is crucial for maximizing gains while minimizing the potential for setbacks. Ignoring safety protocols can lead to significant time away from training and potentially long-term health issues.Weight training injuries often stem from a combination of factors, including improper form, excessive weight, insufficient warm-up, and inadequate recovery.
Understanding these contributing factors is the first step toward building a safe and effective training program.
Common Weight Training Injuries and Their Causes
Musculoskeletal injuries are prevalent in weight training. These range from minor strains and sprains to more serious conditions like tendonitis, rotator cuff tears, and lower back pain. Improper lifting technique is a leading cause, placing undue stress on joints and muscles. For example, rounding the back during squats or deadlifts can compress the spine, leading to lower back pain or even herniated discs.
Similarly, using excessive weight before the body is adequately prepared can result in muscle strains or tears. Ignoring pain signals and pushing through injuries only exacerbates the problem, potentially leading to chronic conditions. Overtraining, insufficient rest, and dehydration also contribute to the risk of injury.
Preventative Measures for Injury Minimization
Implementing a comprehensive injury prevention strategy is paramount. This starts with a proper warm-up, which increases blood flow to muscles, improves flexibility, and prepares the body for the demands of weight training. A dynamic warm-up, incorporating movements like arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists, is recommended. Conversely, a cool-down, including static stretches held for 15-30 seconds per muscle group, helps reduce muscle soreness and promotes recovery.
Focusing on correct form during each exercise is crucial. Starting with lighter weights to master the technique before progressively increasing the load is essential. Progressive overload, gradually increasing the weight, repetitions, or sets over time, challenges the muscles and promotes strength gains without overwhelming the body. Adequate rest and recovery between workouts allows the body to repair and rebuild muscle tissue, minimizing the risk of overuse injuries.
Listening to one’s body and taking rest days when needed is critical. Finally, seeking guidance from a qualified fitness professional can provide personalized instruction and ensure proper technique.
Safety Guidelines for Weight Training, Weight Training Activities
Prioritizing safety is essential for a successful and injury-free weight training program. The following guidelines should be consistently followed:
- Always warm up before each workout and cool down afterward.
- Use proper lifting techniques and avoid using excessive weight.
- Maintain a controlled breathing pattern throughout each exercise.
- Use spotters when lifting heavy weights, particularly during exercises like bench presses and squats.
- Never lift weights when fatigued or injured.
- Ensure adequate hydration before, during, and after workouts.
- Wear appropriate footwear and clothing.
- Maintain a clean and organized workout area.
- Listen to your body and take rest days when needed.
- Consult a healthcare professional or certified personal trainer before starting any new exercise program.
Weight Training Equipment and Resources: Weight Training Activities
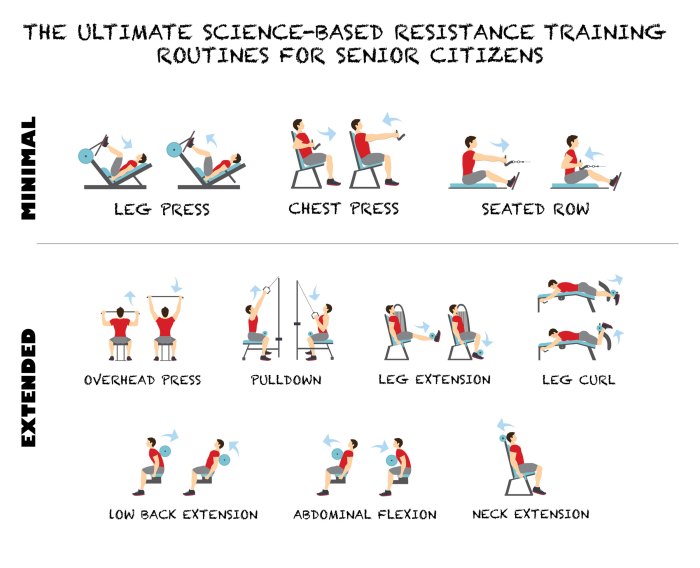
Selecting the appropriate weight training equipment is crucial for achieving fitness goals safely and effectively. The choice depends on individual preferences, experience levels, and available resources. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of different equipment types allows for informed decisions leading to optimized workout routines.
Types of Weight Training Equipment
Weight training utilizes various equipment categories, each offering unique benefits and drawbacks. Free weights, weight machines, and resistance bands represent the primary options. Free weights, encompassing dumbbells and barbells, demand greater balance and coordination, fostering improved neuromuscular control and functional strength. However, they require proper technique to avoid injury. Weight machines offer a guided movement, reducing the risk of injury, but may limit the range of motion and muscle activation compared to free weights.
Resistance bands provide a portable and versatile option, offering variable resistance levels suitable for various exercises and fitness levels. Their affordability and space-saving nature make them attractive, though the resistance offered may not be suitable for all individuals or advanced training programs.
Resistance Band Types and Uses
Resistance bands are categorized by their resistance level (typically indicated by color-coding) and material. Different types cater to varying strength levels and exercise goals.
| Band Type | Resistance Level | Typical Uses | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light (e.g., yellow or green) | Low | Warm-ups, rehabilitation exercises, low-impact workouts | Easy to use, suitable for beginners | Limited resistance for strength training |
| Medium (e.g., red or blue) | Moderate | Strength training, flexibility exercises, dynamic stretches | Versatile, suitable for various exercises | May not be sufficient for advanced users |
| Heavy (e.g., black or purple) | High | Advanced strength training, power exercises | Provides significant resistance for strength gains | Requires significant strength and control |
| Loop Bands | Variable (depending on manufacturer and color) | Leg exercises, glute activation, upper body exercises | Compact, versatile, easy to store | Can be less durable than flat bands |
| Flat Bands | Variable (depending on manufacturer and color) | Pulling exercises, shoulder work, resistance training | Durable, good for various exercises | Less compact than loop bands |
Finding Qualified Fitness Professionals
Access to qualified fitness professionals is essential for safe and effective weight training. Several resources facilitate the search for certified trainers. Professional organizations, such as the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) and the National Strength and Conditioning Association (NSCA), maintain directories of certified professionals. Online platforms and fitness centers often list credentials and qualifications of their trainers.
Checking for certifications and experience ensures individuals receive guidance from competent and knowledgeable professionals. Thorough background checks and client testimonials can also provide additional assurance of a trainer’s reliability and expertise.
Mastering weight training involves a multifaceted approach encompassing proper technique, strategic program design, and mindful attention to nutrition and recovery. By understanding the principles Artikeld in this guide—from selecting appropriate exercises and tailoring programs to individual goals to prioritizing safety and injury prevention—individuals can harness the transformative power of weight training to achieve their fitness aspirations. Remember to consult with a qualified professional before starting any new fitness regimen, particularly if you have pre-existing medical conditions.
The journey to a stronger, healthier you begins with informed choices and consistent effort.

