Strength Training To Lose Fat isn’t just a catchy phrase; it’s a scientifically backed approach to achieving a leaner physique. This guide delves into the metabolic mechanisms that make strength training so effective for fat loss, exploring how it boosts resting metabolism, improves insulin sensitivity, and triggers hormonal changes that favor fat burning over fat storage. We’ll dissect the science, craft a tailored strength training program, and provide nutritional strategies to maximize your results.
From designing a 12-week program for beginners to addressing common misconceptions about muscle growth in women, we cover all the bases. We’ll also examine the importance of proper form in exercises like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and pull-ups, and show you how to track your progress and make necessary adjustments along the way. This isn’t just about losing weight; it’s about building a stronger, healthier, and more efficient you.
The Science Behind Strength Training for Fat Loss: Strength Training To Lose Fat
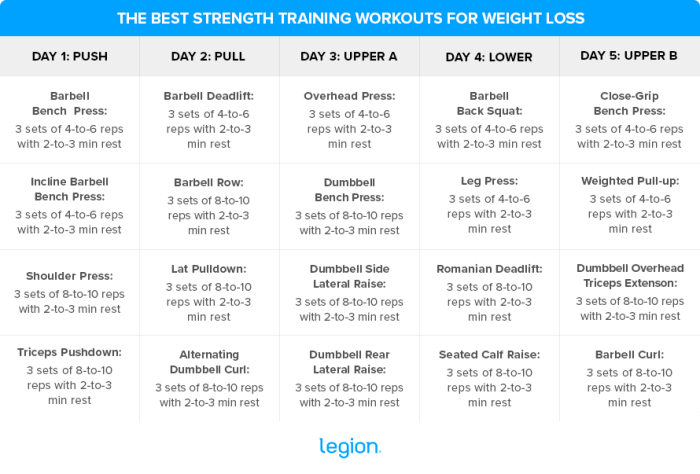
Strength training, often overlooked in fat loss strategies, offers a potent combination of metabolic and hormonal benefits that significantly enhance the body’s ability to shed fat. Contrary to popular belief, cardiovascular exercise alone may not be the most efficient approach. Integrating strength training into a comprehensive fitness plan maximizes results by addressing both fat burning and muscle building.
Metabolic Effects of Strength Training on Fat Burning
Strength training elevates metabolism through several mechanisms. The immediate post-exercise metabolic rate (EPOC), or “afterburn effect,” is significantly higher following resistance training compared to cardio. This means your body continues burning calories at an increased rate even after you’ve finished your workout. Furthermore, strength training stimulates the release of growth hormone, a crucial hormone involved in lipolysis, the breakdown of stored fat.
The increased energy expenditure during and after a strength training session contributes directly to fat loss, particularly when combined with a balanced calorie deficit. Studies have shown that individuals engaging in strength training experience a greater overall calorie expenditure compared to those who solely rely on cardio.
The Role of Muscle Mass in Increasing Resting Metabolic Rate
Muscle tissue is metabolically active; it requires more energy to maintain than fat tissue. Increasing muscle mass through strength training, therefore, directly increases your resting metabolic rate (RMR). RMR represents the number of calories your body burns at rest to maintain basic bodily functions. A higher RMR means you burn more calories even when inactive, facilitating fat loss over time.
For instance, an individual with a higher percentage of muscle mass will burn more calories while sleeping or sitting than someone with a lower muscle mass, even if both individuals weigh the same. This effect contributes significantly to long-term fat loss, making it a sustainable approach to weight management.
Strength Training and Improved Insulin Sensitivity, Strength Training To Lose Fat
Insulin resistance, a hallmark of metabolic syndrome, impairs the body’s ability to effectively utilize glucose, leading to increased fat storage. Strength training significantly improves insulin sensitivity. This means your body becomes more efficient at utilizing glucose for energy, reducing the amount of glucose stored as fat. Improved insulin sensitivity not only aids in fat loss but also reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Studies have consistently demonstrated that resistance training programs improve glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, making it a valuable tool in managing metabolic health and promoting fat loss.
Hormonal Changes Induced by Strength Training and Their Impact on Fat Loss
Strength training triggers the release of anabolic hormones, including testosterone and growth hormone. Testosterone plays a crucial role in muscle protein synthesis, promoting muscle growth and increasing metabolic rate. Growth hormone stimulates lipolysis, the breakdown of fat cells, and reduces fat storage. These hormonal changes contribute significantly to fat loss by increasing muscle mass and enhancing the body’s ability to mobilize and utilize stored fat for energy.
The synergistic effect of these hormonal changes, coupled with the metabolic benefits of strength training, makes it an exceptionally effective strategy for fat loss. The magnitude of these hormonal responses varies depending on factors such as training intensity, volume, and individual characteristics. However, consistent strength training consistently demonstrates a positive influence on hormonal profiles conducive to fat loss.
Ultimately, the journey to losing fat through strength training is a personalized one. By understanding the science behind muscle growth and fat loss, tailoring a program to your fitness level, fueling your body correctly, and consistently monitoring your progress, you can achieve sustainable results. Remember, consistency and proper form are key to maximizing the benefits of strength training, paving the way for a leaner, stronger, and healthier you.
This holistic approach, encompassing exercise, nutrition, and mindful monitoring, provides a powerful strategy for long-term success.

