Top Weight Lifting Exercises are crucial for building strength, muscle mass, and overall fitness. This guide delves into the fundamentals of weightlifting, exploring both compound and isolation exercises, proper form, and injury prevention strategies. We’ll cover essential exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses, alongside targeted isolation movements to sculpt your physique. Understanding progressive overload and choosing the right training split are also key components to maximizing your results and avoiding injury.
From beginner tips to advanced programming considerations, this comprehensive resource equips you with the knowledge and tools to create a safe and effective weightlifting program tailored to your fitness goals. Whether you’re aiming for increased strength, muscle hypertrophy, or improved endurance, this guide provides the framework for success. We’ll explore different training splits, explain how to adjust weight and reps based on progress, and detail strategies to prevent common weightlifting injuries.
Introduction to Weight Lifting Exercises

Weightlifting, encompassing a range of exercises using resistance to build muscle mass and strength, offers a multitude of health benefits beyond mere aesthetics. Regular weight training improves bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis; enhances metabolism, aiding in weight management; and strengthens joints and connective tissues, contributing to overall physical resilience. Furthermore, it positively impacts mental well-being, reducing stress and improving mood.Proper form and technique are paramount in weightlifting.
Incorrect execution can lead to injuries ranging from minor muscle strains to severe joint damage. Focusing on controlled movements, maintaining proper posture, and utilizing a full range of motion are critical for maximizing results and minimizing the risk of harm. Learning the correct techniques from qualified instructors or reliable resources is a crucial first step for any aspiring weightlifter.
Beginner Weightlifting Program Guidelines
Beginners should prioritize establishing a solid foundation of proper form before increasing weight or intensity. A gradual progression, focusing on mastering fundamental movements, is essential to prevent injury and promote long-term success. Starting with lighter weights and higher repetitions allows for better muscle activation and control, building strength and endurance without compromising form. A well-structured program should incorporate compound exercises, such as squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and overhead presses, which work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, maximizing efficiency.
Rest and recovery are also crucial elements; allowing muscles adequate time to repair and rebuild is essential for growth and avoiding overtraining. A balanced diet supporting muscle growth and recovery should complement the training regimen.
Exercise Selection and Progression
A well-rounded weightlifting program incorporates a variety of exercises targeting different muscle groups. This approach promotes balanced muscular development and reduces the risk of muscle imbalances. Beginners should focus on mastering fundamental movements before progressing to more advanced exercises. Progressive overload, gradually increasing the weight, repetitions, or sets over time, is essential for continued muscle growth and strength gains.
This gradual increase challenges the muscles, stimulating adaptation and growth. For example, if an individual can comfortably perform three sets of ten repetitions of a particular exercise with a specific weight, they might increase the weight slightly the following week, maintaining the same number of sets and repetitions. This systematic approach ensures continuous progress and avoids plateaus.
Safety Precautions and Considerations
Prioritizing safety is crucial in any weightlifting program. Always warm up before each workout to prepare the muscles and joints for activity. This warm-up could involve light cardio and dynamic stretching. Similarly, a cool-down period following the workout helps reduce muscle soreness and promote recovery. This cool-down might consist of static stretching, holding each stretch for 20-30 seconds.
Using proper lifting techniques, such as maintaining a stable core and avoiding jerky movements, is essential to minimize the risk of injury. Furthermore, seeking guidance from a qualified fitness professional can provide personalized advice and ensure proper form. If any pain is experienced during a workout, the exercise should be stopped immediately. Finally, listening to one’s body and adjusting the program based on individual needs and progress is crucial for long-term success and injury prevention.
Compound Exercises: Top Weight Lifting Exercises
Compound exercises, those that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, are the cornerstone of any effective weightlifting program. Their superiority over isolation exercises, which focus on a single muscle group, lies in their superior efficiency and overall strength gains. By working several muscle groups concurrently, compound exercises promote greater hormonal responses, leading to amplified muscle growth and increased metabolic rate.
This translates to a more efficient workout and faster progress towards fitness goals.
Benefits of Compound Exercises Over Isolation Exercises
Compound exercises elicit a greater anabolic response, stimulating the release of hormones like testosterone and growth hormone, crucial for muscle growth and strength development. This hormonal surge is significantly less pronounced during isolation exercises. Furthermore, compound movements improve functional strength, mimicking real-world movements like lifting, pushing, and pulling, leading to better overall physical performance in daily life. Isolation exercises, while useful for targeted muscle development, lack this holistic benefit.
The increased calorie burn during compound exercises also contributes to fat loss, making them an efficient tool for body recomposition.
Comparison of Squats, Deadlifts, and Bench Presses
The squat, deadlift, and bench press are arguably the three most effective compound exercises. Squats primarily target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, building lower body strength and power. The deadlift, a full-body movement, engages the entire posterior chain—from the traps and lats to the hamstrings and glutes—developing explosive power and overall strength. The bench press, a fundamental upper body exercise, focuses on the chest, shoulders, and triceps, improving pushing strength and upper body mass.
While each exercise has its primary focus, all three contribute significantly to overall strength and muscle growth, making them synergistic when combined in a training program. The differences lie primarily in the muscle groups emphasized and the movement patterns involved.
Sample Workout Routine Incorporating Squats, Deadlifts, and Bench Presses
A balanced routine incorporating these three exercises should prioritize proper form and progressive overload. A sample three-day split could look like this: Day 1: Squats (variations), accessory lower body exercises; Day 2: Deadlifts (variations), accessory back and core exercises; Day 3: Bench Press (variations), accessory upper body exercises. Rest days are crucial for muscle recovery and growth. The specific number of sets and repetitions will depend on individual goals and experience levels.
Always prioritize proper form over lifting heavy weight.
Muscles Worked, Equipment, and Variations
| Exercise | Muscles Worked | Equipment Needed | Variations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squat | Quadriceps, Hamstrings, Glutes, Core | Barbell, Weight Plates, Squat Rack (optional) | Barbell Back Squat, Front Squat, Goblet Squat, Overhead Squat |
| Deadlift | Traps, Lats, Erector Spinae, Glutes, Hamstrings, Forearms | Barbell, Weight Plates | Conventional Deadlift, Sumo Deadlift, Romanian Deadlift (RDL) |
| Bench Press | Pectorals, Anterior Deltoids, Triceps | Barbell, Weight Plates, Bench | Barbell Bench Press, Incline Bench Press, Decline Bench Press, Dumbbell Bench Press |
Isolation Exercises
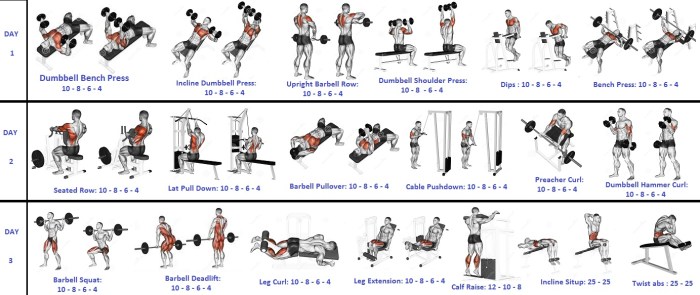
Isolation exercises, unlike compound movements, target individual muscle groups, promoting focused hypertrophy and addressing specific muscle weaknesses. They are crucial for sculpting physique and improving muscle definition, often used in conjunction with compound exercises for a comprehensive training program. Proper form is paramount to prevent injury and maximize results.
Chest Isolation Exercises
Three effective chest isolation exercises are cable flyes, dumbbell flyes, and pec deck flyes. Cable flyes involve using a cable machine to perform a fly motion, targeting the pectoral muscles with consistent tension throughout the movement. Dumbbell flyes, performed on a bench, allow for a greater range of motion and emphasize the stretch at the bottom of the movement.
The pec deck machine provides a controlled, targeted movement that minimizes the involvement of secondary muscles.
- Cable Flyes: Proper form involves maintaining a slight bend in the elbows, controlling the weight throughout the movement, and focusing on the contraction of the pectoral muscles. Advantages include consistent tension and targeted muscle activation. Disadvantages include potential strain on the shoulder joints if performed incorrectly.
- Dumbbell Flyes: Maintain a controlled tempo, avoiding momentum. Advantages include a greater range of motion and the ability to adjust weight unilaterally. Disadvantages include requiring greater balance and coordination.
- Pec Deck Flyes: Focus on the contraction at the end of the movement. Advantages include a controlled and isolated movement. Disadvantages include limited range of motion compared to dumbbell or cable flyes.
Back Isolation Exercises
Lat pulldowns (close grip), face pulls, and seated cable rows effectively isolate back muscles. Close-grip lat pulldowns emphasize the lower lats, face pulls target the rear deltoids and upper back, while seated cable rows focus on the mid-back muscles.
- Close-Grip Lat Pulldowns: Maintain a controlled descent, focusing on the contraction of the lats. Advantages include targeted lat activation and a controlled movement. Disadvantages include potential strain on the wrists if improper form is used.
- Face Pulls: Retract your shoulder blades throughout the movement. Advantages include improved posture and shoulder health, along with targeting the rear deltoids and upper back. Disadvantages include needing to adjust the cable height for optimal form.
- Seated Cable Rows: Maintain a straight back and controlled movement. Advantages include targeted mid-back activation and controlled resistance. Disadvantages include potential rounding of the back if form is compromised.
Shoulder Isolation Exercises
Lateral raises, front raises, and reverse flyes are key shoulder isolation exercises. Lateral raises target the medial deltoids, front raises focus on the anterior deltoids, and reverse flyes emphasize the posterior deltoids.
- Lateral Raises: Keep a slight bend in the elbows and control the weight throughout the movement. Advantages include targeted medial deltoid development. Disadvantages include potential for shoulder impingement if performed incorrectly.
- Front Raises: Similar to lateral raises, control the weight and avoid swinging. Advantages include targeted anterior deltoid development. Disadvantages include potential for shoulder impingement.
- Reverse Flyes: Maintain a straight back and focus on the squeeze at the top of the movement. Advantages include targeting the posterior deltoids, improving posture and shoulder balance. Disadvantages include requiring a controlled movement to prevent injury.
Leg Isolation Exercises, Top Weight Lifting Exercises
Leg extensions, hamstring curls, and calf raises isolate the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves respectively.
- Leg Extensions: Focus on the contraction at the top of the movement. Advantages include targeted quadriceps development. Disadvantages include potential for knee strain if performed incorrectly or with excessive weight.
- Hamstring Curls: Maintain a controlled movement and avoid using momentum. Advantages include targeted hamstring development. Disadvantages include potential for hamstring strain if performed incorrectly.
- Calf Raises: Focus on the full range of motion. Advantages include targeted calf development. Disadvantages include potential for ankle strain if performed incorrectly.
Arm Isolation Exercises
Bicep curls (barbell, dumbbell), hammer curls, and triceps extensions (overhead, rope) are effective arm isolation exercises.
- Bicep Curls (Barbell, Dumbbell): Maintain a controlled movement and avoid swinging the weight. Advantages include targeted bicep development. Disadvantages include potential for bicep strain if performed incorrectly.
- Hammer Curls: Focus on the contraction at the top of the movement. Advantages include targeting both the biceps and brachialis muscles. Disadvantages include potentially less bicep activation compared to standard curls.
- Triceps Extensions (Overhead, Rope): Control the weight throughout the movement. Advantages include targeted triceps development. Disadvantages include potential for elbow strain if performed incorrectly.
Mastering weightlifting requires dedication, proper technique, and a well-structured program. By understanding the principles of compound and isolation exercises, progressive overload, and injury prevention, you can safely and effectively achieve your fitness objectives. Remember to prioritize proper form, listen to your body, and gradually increase the intensity of your workouts to maximize gains while minimizing the risk of injury. Consistent effort and a smart approach are the keys to unlocking your full potential in the world of weight training.

